Introduction:
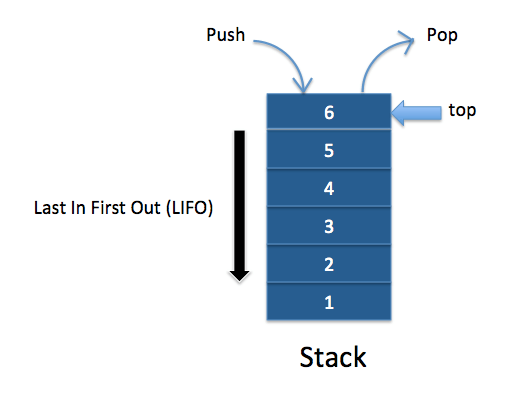
Stack is a most commonly used linear data structure. It follows the LIFO i.e.
Last In First Out rules which means the insertion,
deletion and other operations are performed on the top element.
By means of top element of the stack is the last element inserted onto the
stack in a nonempty stack.
Operations on Stack:
- Push: to inset element(s) onto the stack.
- Pop: to delete the top element of the stack.
-
isEmpty: to check if the stack is going through the underflow
condition.
-
isFull: to check if the stack is going through the overflow
condition.
- Peek: this operation is done to query about the top element of the stack.
We can implement a stack using an array or using the linked list. Stack implement using a linked list is also known as linked stack.
Here we will see the stack using the array implementation.
/************************************************************************
* Implementation of stack using an array *
*************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX 10
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
typedef struct{
int top;
int element[MAX];
}stack;
//Function prototypes...
void createStack(stack *);
void push(stack *, int);
int pop(stack *);
int peek(stack *);
bool isEmpty(stack *);
bool isFull(stack *);
//Main Function.............................................
int main(){
stack s;
createStack(&s);
while(1){
int ch, value;
printf("\n++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n");
printf("\tAvailable Options :");
printf("\n++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
printf("\n\t1. Push
\n\t2. Pop
\n\t3. Peek
\n\t4. Exit
\n\t5. Show the Stack
\nChoose your option(1 - 5):\t");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch(ch){
case 1: //Push Operation...
//checking for overflow...
if(isFull(&s)){
printf("\n-->Stack is full. Items can not be insrted...\n");
}else{
//Inserting the element...
printf("\nEnter the vlaue to be inserted:\t");
scanf("%d", &value);
push(&s, value);
printf("\n-->%d is inserted into the stack...\n", value);
}
break;
case 2: //Pop
if(isEmpty(&s)){
printf("\n-->Nothing to pop from the stack...\n");
}else{
printf("\n-->%d is popped out from the stack...\n", pop(&s));
}
break;
case 3: //Peek
printf("\n-->Element at the top is:\t%d\n", peek(&s));
break;
case 4: //Exit
exit(0);
break;
case 5: //Showing the full stack...
if(s.top == -1){
printf("\n-->Empty Stack...\n");
}else{
printf("-->");
for(int i = 0; i <=(s.top); i++){
printf("%d ", s.element[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
break;
default:
printf("\n-->************Error Occured!**********\n");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
//Function Definitions......................................
//Creating an empty stack...
void createStack(stack *ps){
ps->top = -1;
}
//Inserting an element in the stack...
void push(stack *ps, int value){
ps->element[++ps->top] = value;
}
//Checking for if stack is full...
bool isFull(stack *ps){
if(ps->top == (MAX - 1)){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//Checking if stack is empty...
bool isEmpty(stack *ps){
if(ps->top == -1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//Removing an item from the stack..
int pop(stack *ps){
int item;
item = ps->element[ps->top];
//printf("%d is popped out from the stack", item);
ps->top--;
return item;
}
//Peek function...
int peek(stack *ps){
int elm;
elm = ps->element[ps->top];
return elm;
}